The gateway supports the SMPP (Short Message Peer to Peer) protocol, version 3.3 or 3.4, to connect to an SMSC over the internet or other private TCP/IP network. As SMPP is designed and optimised specifically for SMS transmission, many mobile operators provide SMPP connections for higher volumes of SMS traffic.
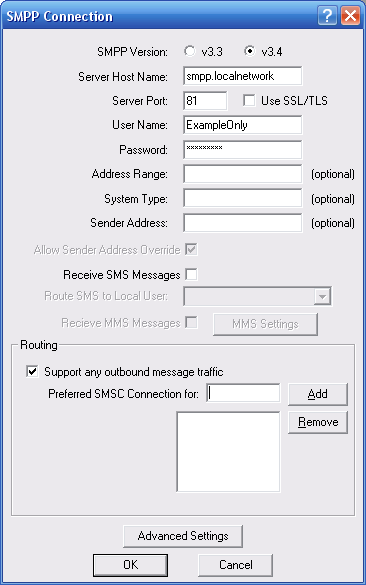
To add an SMPP connection, select “Add” from the “SMSC” configuration dialog. Then select “SMPP over TCP/IP“.
“SMPP Version” specifies the version of the SMPP protocol to use. The gateway supports “v3.3” and “v3.4”.
“Server Host Name” specifies the TCP/IP address or host name of the SMPP server.
“Port” specifies the TCP/IP port on the SMPP server to which the gateway should connect.
“Use SSL/TLS” should only be checked if the service provider specifically indicates that they support SSL or TLS encryption for the SMPP connection.
“User Name” specifies the user name (sometimes called System ID) for the gateway to use when connecting to the SMPP server.
“Password” specifies the password for the gateway to use when connecting to the SMPP server.
“Address Range” is a parameter used primarily when receiving messages. Set this field only if instructed to do so by your SMPP service provider.
“System Type” is an optional login parameter that should be set only if required by the SMPP server. The SMPP system administrator will provide this value, which when required, is usually a short text string.
“Sender Address” specifies the default sender address (phone number) to apply to outbound SMS messages. The SMPP server may override this setting.
Check “Allow Sender Address Override” if you want to allow messages submitted to the gateway to be able to specify a sender address. If this box is checked, and a sender address is present in a message being submitted to an SMPP based SMSC, the sender address in the message will be submitted to the SMSC. The SMPP server may override this setting.
Check the “Receive SMS Messages” box if you wish to receive messages from the SMPP server. When this box is checked, by default, the gateway will connect to the SMPP server with two separate connections, one bound as a transmitter and the other bound as a receiver. Some SMS providers prefer that only a single connection resource is used, bound as a transceiver. It is possible to configure a single transceiver connection to be used on the “Advanced Settings” page.
It is possible to configure NowSMS to route all SMS messages received via this SMSC connection to a user account on the NowSMS server by selecting the user account in the “Route SMS to local user” setting. It is possible for a user to connect to the NowSMS server either using SMPP (an SMS specific protocol) or POP3 (an e-mail protocol). These user accounts are defined on the “SMS Users” page of the NowSMS configuration dialog.
Check the “Receive MMS Messages” box if you will be receiving MMS Notification messages via the SMSC. Note that most service providers do not support the routing of MMS notification messages via an SMSC connection. If MMS messages will be received via the SMSC connection, it is necessary to also configure additional MMS settings. The “MMS Settings” dialog will display a dialog with additional configuration settings that are required for enabling the gateway to be able to receive MMS messages from the operator network. For additional configuration information, please refer to Connecting to an Operator MMSC – Using a GPRS Modem. For additional configuration information on processing received MMS messages, please refer to 2-Way MMS Support.
The “Routing” group of options is used when multiple SMSC connections are defined to the gateway. These options define what messages should be routed to this connection. The Routing options are common to SMPP, GSM Modem, UCP/EMI and HTTP connections, and are described in the Routing Options section.
When the “OK” button is selected, the gateway will attempt to connect to the SMPP server to verify the configuration information provided. Diagnostic information will be displayed if the connection fails. The connection will only be added to the configuration after a successful connection to the SMPP server.
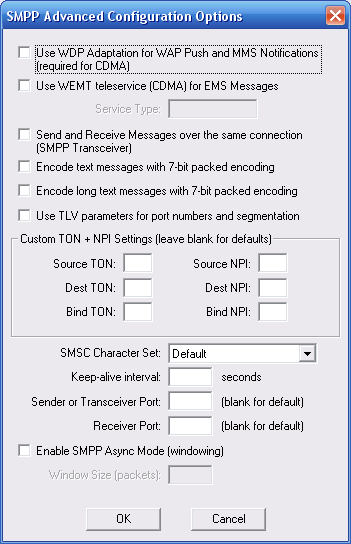
Many SMPP SMSC providers will also tell you to that you need to configure certain additional parameters in your SMPP software. (Editor’s Note: Or many won’t tell you, and you have to make educated guesses.) NowSMS provides the ability to configure these settings on the SMPP Advanced Configuration Options dialog, accessible by pressing the Advanced Settings button when defining properties for an SMPP connection.
Use WDP Adaptation for WAP Push and MMS Notifications (required for CDMA) – This setting is primarily used when connecting to a CDMA based SMSC. By default, NowSMS generates WAP Push messages (and MMS Notification messages which are based upon WAP Push) using a format that is specific to GSM (and WCDMA/UMTS) environments. When this configuration option is enabled, NowSMS uses a protocol independent format known as “WDP Adaptation”. This is usually the only practical option for delivering WAP Push messages in a CDMA environment. In this case, NowSMS will submit messages to the SMPP server using the “WAP” teleservice (SMPP service type). For more information on this option, please refer to the NowSMS Technical Bulletin titled “Using NowSMS as an MMSC in CDMA or CDMA2000 Environments“.
Use WEMT teleservice (CDMA) for EMS Messages – This setting is primarily used when connecting to a CDMA based SMSC. When NowSMS detects that a message is of the EMS format, it will submit the message to the SMPP server using the specified Service Type value (usually WEMT).
Send and Receive Messages over the same connection (SMPP Transceiver) – By default, when NowSMS is configured to both send and receive messages via an SMPP connection, NowSMS will connect to the SMPP server with two separate connections, one bound as a transmitter and the other bound as a receiver. Some SMS providers prefer that only a single connection resource is used, bound as a transceiver. When this option is enabled, NowSMS will use a single transceiver connection instead of two separate connections.
Encode text messages with 7-bit packed encoding – In GSM environments, when messages are actually delivered to a handset, simple text messages are compacted into a 7-bit packed encoding. (This allows 160 text characters to fit into 140 binary bytes of data.) Normally, in SMPP environments, this compaction is performed by the SMSC. However, if you receive garbage text messages when sending via NowSMS, try enabling this setting which will cause NowSMS to perform the compaction when submitting via the SMPP server. (This is normally only required for SMPP 3.3 servers.)
Encode long text messages with 7-bit packed encoding – Similar to the above setting, this setting applies only for long messages (and potentially other messages such as EMS, which include UDH elements). Some SMSCs expect normal text messages to be encoded use regular text encoding. However, if the message includes any UDH elements, the SMSC treats it as a binary message and assumes that any 7-bit packing of the text has already been performed. If you receive garbage messages when sending longer text messages via NowSMS, try enabling this setting.
Use TLV parameters for port numbers and segmentation – By default, when sending long text messages which must be segmented over multiple SMS messages, or when sending messages that include port numbers such as for WAP push, NowSMS automatically generates the appropriate GSM User Data Header (UDH) fields. When this option is enabled, NowSMS will instead use optional TLV parameters in the SMPP header for port numbers and segmentation. Specifically port numbers will be encoded in the source_port and destination_port parameters, and segmentation will be encoded in the sar_msg_ref_num, sar_total_segments, and sar_segment_seqnum parameters.
Custom TON + NPI Settings
Your SMS provider might be tell you to specify particular Bind TON, Bind NPI, Source TON, Source NPI, Destination TON or Destination NPI values. (TON = Type Of Number, NPI = Numbering Plan Indicator)
The Now SMS & MMS Gateway uses intelligent defaults for the TON and NPI values which are sufficient for 99% of SMPP connections.
The Source TON and NPI are settings that apply to the sender address that is associated with messages that are submitted by the Now SMS & MMS Gateway to the SMSC.
NowSMS automatically sets the Source TON to “1” if the sender address is in international format (starts with a “+” character), and the Source NPI to “1”.
If the sender address is not in international format, NowSMS checks the to see if the address contains alphabetic characters. If it does, then it is considered to be an alphanumeric sender, and the Source TON is automatically set to “5”, with Source NPI” set to “0”.
Next NowSMS checks to see if the address is 5 digits or less, if it is, then it is considered to be a short code, and the Source TON is automatically set to “3”, and Source NPI to “0”. (To change the default max short code length, or to disable this check, edit SMSGW.INI, and add MaxSMPPShortCodeLen=# under the [SMSGW] header. Addresses that are this number of digits or less are considered to be short codes.)
If the above checks are still not satisfied, NowSMS automatically sets the Source TON to “0”, and the Source NPI is set to “1”.
The Destination TON and NPI are settings that apply to the recipient addresses for messages that are submitted by the Now SMS & MMS Gateway to the SMSC. NowSMS automatically sets the Destination TON to “1” if the recipient address is in international format (starts with a “+” character). If the recipient address is not in international format, NowSMS automatically sets the Destination TON to “0”. In both cases, the Source NPI is set to “1”.
If it is necessary to adjust these TON and NPI settings, they can be adjusted via the Custom TON + NPI Settings section.
If a TON or NPI value is explicitly set in the SMSGW.INI file, this value will be used in place of the automatic determination described above.
The Bind TON and Bind NPI settings are used when binding to the SMSC only. By default, NowSMS will use 0 for both values.
SMSC Character Set – By default, NowSMS uses the GSM character set when submitting SMS messages via SMPP, and it indicates via the data_coding parameter that the default encoding is used. If you experience a problem where @ symbols and other characters do not appear correctly in messages, your SMSC might be expecting a different character set. Assuming that you are working in a GSM environment primarily, first try changing this setting to “IA5 (GSM)”. When this setting is applied, NowSMS will still use the GSM character set, but it will set a flag in the header to indicate this. If the character problems persist, change this setting to “iso-8859-1 (Latin)”, which is the standard character set used in Western Europe.
Keep-alive Interval – This setting specifies a value, in number of seconds, between which NowSMS will automatically send enquire_link commands to the SMSC. Most SMSC require that connected clients periodically send an enquire_link command to verify that they are still connected and functioning correctly. If this parameter is not specified, a default of 58 seconds is used. A value of 0 seconds can be used to disable NowSMS from sending any enquire_link commands.
Sender or Transceiver Port – Some SMSCs have firewall restrictions which will only allow you to connect to the SMSC from a specific IP address and a specific port number. Normally, NowSMS will use a dynamically allocated port number when connecting to an SMSC. However, this setting allows the port number to be fixed. This setting applies to the port number to be used for the connection that uses the transmitter (send) or transceiver SMPP bind. ( Note: If you use fixed port numbers, after disconnecting from an SMSC, it may take up to 5 minutes before you are allowed to reconnect. This is a TCP/IP limitation on reconnects after a disconnect when the same source and destination ports are used for the reconnection attempt.)
Receiver Port -Similar to the “Sender or Transceiver Port” setting, this fixed port number is applied to the connection that is used for the receiver SMPP bind.
Enable SMPP Async Mode (windowing) – Enabling this setting allows messages to be sent more rapidly over an SMPP connection. The typical SMPP message flow involves the sender submitting a message to the server, and the receiver sending back a response to acknowledge receipt of the message. When async mode is not enabled, the sender does not send the next message until the previous acknowledgment has been received. Depending on the speed (and latency) of the connection between the sender and the receiver, and the amount of processing that the receiver performs before sending back an acknowledgment, this can have a serious impact on the overall connection performance. Enabling SMPP Async Mode tells NowSMS that it does not need to wait for an acknowledgment for the previous message before submitting the next message. Instead, NowSMS will send up to the defined Window Size number of messages without receiving an acknowledgment. As long as this is properly supported by the SMS service provider, this can provide a great increase in potential throughput, and is generally required for any single SMPP connection to exceed 3 messages per second.